Radar Systems
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
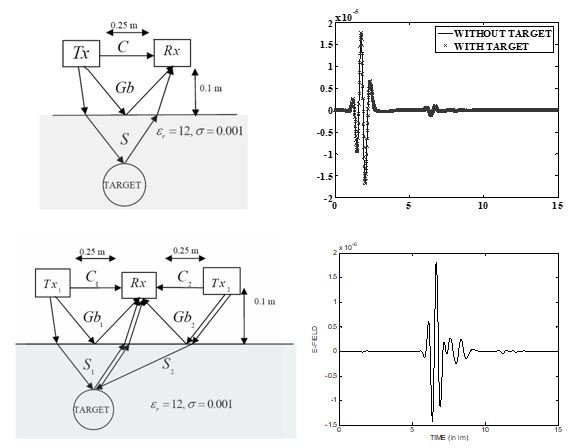
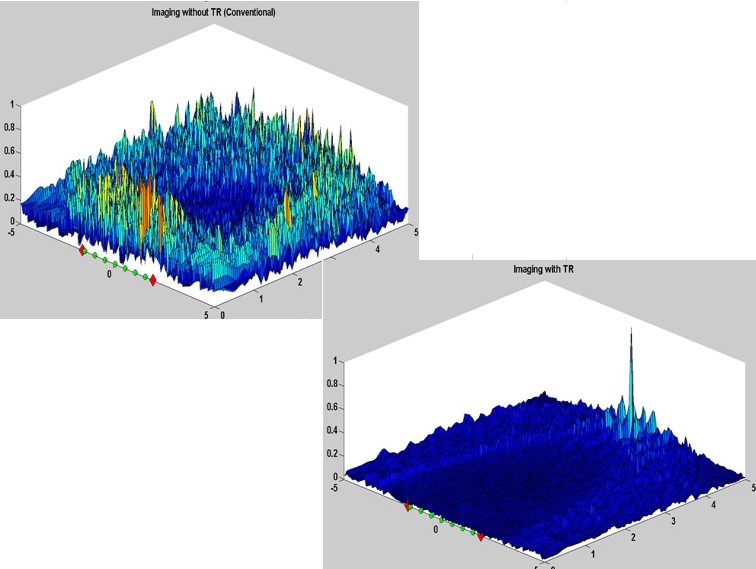
GPR is one of the established non-destructive techniques for subsurface deployment. The two antenna GPR system suffers from ground bounce and antenna coupling effects. Proper seclusion and/or design of the antennas can often reduce the antenna coupling effects but it is difficult to separate the ground bounce effects from the target response. Instead a system with two transmitters and one receiver placed in between them is designed.
Through-Wall Sensing Radar (TWIR)
TWIR research is focused on the analysis of EM propagation through barrier, in the design of UWB antennas, in signal processing for detection, localization and tracking as well as in image processing for classification. Some issues with existing TWIR systems include poor cross range resolution, formation of blurred and ghost images due to multipath, weak target detection due to heavy attenuation at the wall, masking of near wall target, obscured desired target (shadowing) and poor target classification.
MM-wave Radar
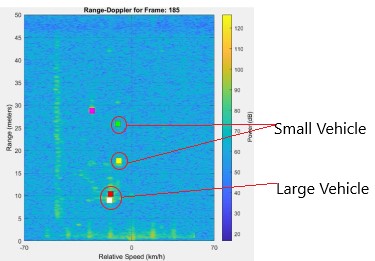
Mm-wave radar achieves better velocity resolution and accuracy. Compared to 24 GHz sensors, the 77 GHz sensor improves velocity resolution and accuracy by 3x. Functionalities are further augmented by the use of advanced chirp and frame configurations in software defined radar.
AI in Radar
Autonomous operation of Radar depends on how efficiently it can perceive the environment and adapt to changes in the environment. Airtificial intelligence can help by comparative analysis based on the library of precorded data. AI can also help adapt the system by employing machine learning to acquire experience from actual or generated model applications.
